Opened July 9, 1904, this lift lock is the highest of its type in the world, transferring boats between two water levels in a single 19.8 m (65 ft.) lift. Designed in place of conventional locks, which would have lengthed the time considerably to transverse a gradual drop, this lift lock was a unique solution made feasible. It operates on a balance principle. Each boat chamber is supported by a ram, 2.28 m (7.5 ft.) In diameter. These move up and down inside water-filled cylinders connected by a pipe.
ASME


This is the oldest operating vessel with a diagonal, compound steam engine, with disc valve gear. Operating at a higher pressure than the oscillating-cylinder engines then used in lake steamers, this type of engine was more powerful and efficient, as well as smaller. The compound engine, built by Sulzer brothers of Winterthur, uses super-heated steam from the boilers in two stages-high and low pressure-before exhausting it into a condenser. The engine produces 650 horsepower, turning two paddle wheels.

The N.S. Savannah was the first nuclear-powered cargo-passenger ship, built by the New York Shipbuilding Corporation at Camden, New Jersey. The 74 maximum-power thermal megawatt pressurized-water reactor was supplied by the Babcock & Wilcox Company. Nearly 600 feet long with 22,000-tons displacement, the ship at top speed surged along at 24 knots, with more than 22,300 shaft horsepower to a single propeller. A joint venture by the U.S. Maritime Administration and the Atomic Energy Commission to the design of George G. Sharp Inc.

This machine, designed by Alton S. Newell, efficiently reduced automobile bodies into scrap metal for recycling. A body was fed into the shredder at a controlled rate, and rotating hammers, driven by a 500-hp motor, shredded it into small pieces that were easily shipped. The process took about 10 minutes a car and used less energy than other shredding and crushing machines.


This wind tunnel complex was developed by the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NASA's predecessor) to serve the emerging need for supersonic research and development following World War II. The three-testing-section configuration covers Mach number .03-3.5 and utilizes a single common drive and two compressors.


This reaction or "Scotch" turbine had as its antecedent the steam reaction wheel invented in Greek Alexandra by Hero around 100 B.C.. It found widespread hydraulic application in the United States from the beginning of the nineteenth century to mid-century when French-inspired hydraulic turbine design pushed reaction wheels into obsolence.

The glider was the first heavier-than-air human-carrying aircraft to achieve controlled piloted flight. On his first successful flight, August 28, 1883, John Montgomery soared at about 600 feet. The Montgomery glider's success demonstrated aerodynamic principles and designs fundamental to the modern aircraft.

As a practical conveyance during the horse-and-buggy era, the Monongahela Incline was one of seventeen built and operated in Pittsburgh in the last century. Of the seventeen, the Monongahela and the Duquesne are the only two remaining operating units. While the Mt. Washington Incline was known as a coal-carrying incline plane in 1854, the Monongahela Incline is probably the earliest passenger-carrying incline in the United States and has been in continuous successful service since its construction.

The La Esperanza sugar mill steam engine is one of the few remaining American links to the pioneer beam engines of the English inventors Thomas Newcomen (1712) and James Watt (1769). The engine was built in 1861 in Cold Spring, New York, by the West Point Foundry. The general arrangement and…
Read More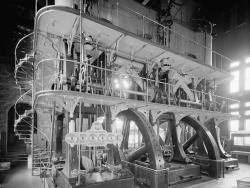
This machine is an unusual triple-expansion, three-crank rocker engine, which in its day was a high-capacity unit providing outstanding performance for the Boston Water Works Corporation. Designed by Erasmus Darwin Leavitt, Jr. (1836-1916), Engine No. 3 was installed in 1894 to a high-service…
Read More

At the mountain where the Civil War's Battle Above the Clouds was waged, tourist business has thrived from the building of its first toll road (Whiteside Pike) in 1857 to present day.
More than 75,000 tourists a year were visiting the site when the war interceded. Tourism was not…
Read More

Designed and constructed in the early 1940s, this laboratory has an unequalled capacity to simulate a wide range of climatic conditions from arctic cold to jungle moisture. Data from tests of some three hundred different aircraft and over two thousand items of equipment has provided information…
Read More
The Old Mill, a smock type of windmill, believed to be the oldest operating windmill in the United States. Most of its parts are original. This mill is the sole survivor of four that once stood along the range of hills west of the town of Nantucket. The long spar and wheel rotate the top of the…
Read More
This pump, designed by Edwin Reynolds (1831-1909) and built by the Edward P. Allis company, is the major component of one of the earliest water-pollution control systems. It was capable of pumping more than a half billion gallons of water a day, the highest-capacity pump in the world when…
Read More
When Ford Motor Company introduced its new Model T on October 1, 1908, even an inveterate optimist like Henry Ford (1863-1947) could not predict the vast changes that his rather homely new vehicle would produce. What flowed from this series of bold innovations was more than an endless stream of…
Read More
As a practical conveyance during the horse-and-buggy era, the Monongahela Incline was one of seventeen built and operated in Pittsburgh in the last century. Of the seventeen, the Monongahela and the Duquesne are the only two remaining operating units. While the Mt. Washington Incline was known…
Read More
The glider was the first heavier-than-air human-carrying aircraft to achieve controlled piloted flight. On his first successful flight, August 28, 1883, John Montgomery soared at about 600 feet. The Montgomery glider's success demonstrated aerodynamic principles and designs fundamental to the…
Read More
This reaction or "Scotch" turbine had as its antecedent the steam reaction wheel invented in Greek Alexandra by Hero around 100 B.C.. It found widespread hydraulic application in the United States from the beginning of the nineteenth century to mid-century when French-inspired hydraulic turbine…
Read More

This wind tunnel complex was developed by the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NASA's predecessor) to serve the emerging need for supersonic research and development following World War II. The three-testing-section configuration covers Mach number .03-3.5 and utilizes a single…
Read More

This machine, designed by Alton S. Newell, efficiently reduced automobile bodies into scrap metal for recycling. A body was fed into the shredder at a controlled rate, and rotating hammers, driven by a 500-hp motor, shredded it into small pieces that were easily shipped. The process took about…
Read More
The N.S. Savannah was the first nuclear-powered cargo-passenger ship, built by the New York Shipbuilding Corporation at Camden, New Jersey. The 74 maximum-power thermal megawatt pressurized-water reactor was supplied by the Babcock & Wilcox Company. Nearly 600 feet long with 22,000-tons…
Read MoreThis is the oldest operating vessel with a diagonal, compound steam engine, with disc valve gear. Operating at a higher pressure than the oscillating-cylinder engines then used in lake steamers, this type of engine was more powerful and efficient, as well as smaller. The compound engine, built…
Read More
Opened July 9, 1904, this lift lock is the highest of its type in the world, transferring boats between two water levels in a single 19.8 m (65 ft.) lift. Designed in place of conventional locks, which would have lengthed the time considerably to transverse a gradual drop, this lift lock was a…
Read More
The Pilatusbahn—the steepest rack railway in the world—has operated successfully since its opening in 1889 over a route of 4.62 kilometers (2.87 miles) between Alpnachstad on Lake Lucerne and Pilatus Kulm, rising 6,791 feet (2,070 meters) above sea level. This results in a gradient of 48%, or a…
Read More

