Amos Eaton and Stephen Van Rensselaer founded the Rensselaer School for "the application of science to the common purposes of life" in 1824. Eaton had practiced surveying as a teenager building his own compass and chain and wrote an early book on surveying. Later he studied law before becoming interested in geology and agriculture. Stephen Van Rensselaer was the seventh patroon of Rensselaerwyck a track of land comprising most of the current Rensselaer, Albany and Columbia Counties in the State of New York.
1800-1829


Morris Canal was built to transport coal from the Lehigh Valley of Pennsylvania to industrial markets in Newark and New York. The total length of the canal was 106 miles. The canal climbed an astonishing 914 feet from Newark Bay to the summit at Lake Hopatcong, and then dropped 760 feet to the Delaware River at Phillipsburg. This gave the canal an average vertical slope of 18 feet per mile, steep compared to the contemporary Erie Canal's relatively gentle slope of one foot per mile.

The Granite Railway Company of Quincy was the first commercial railway in the United States. Incorporated in 1826 and designed by Gridley Bryant, the railway relied on horses, rather than steam locomotives, to draw the cars along the tracks. Its primary purpose was to transport granite from Quincy to build the Bunker Hill Monument.

Between 1825 and 1847 the State of Ohio constructed 1,000 miles of canals and feeder canals, 33,000 acres of reservoir surface area, 29 dams across streams, 294 lift locks, 44 aqueducts and many smaller structures at a cost of about 16 million dollars. The network of navigable canals provided a system of economical transportation where none had previously existed; the young state, with its isolated frontier lifestyle, was transformed almost overnight into a thriving segment of the nation's economy.

The Wilkinson Mill, situated on the west bank of the Blackstone River in Pawtucket, was built between 1810 and 1811 by machinist Oziel Wilkinson. Constructed in stone rubble, three and one-half stories high, the mill played a critical role in the history of textile technology, in steam power generation, and in the development of the machine tools industry. The Wilkinson family came to Pawtucket in the 1780s and set up a shop to forge anchors, build presses for oil works, and mold iron screws used in paper pressing machinery.

The Wilkinson Mill, situated on the west bank of the Blackstone River in Pawtucket, was built between 1810 and 1811 by machinist Oziel Wilkinson. Constructed in stone rubble, three and one-half stories high, the mill played a critical role in the history of textile technology, in steam power generation, and in the development of the machine tools industry.

According to oral history, George Washington visited the canal diggings in 1792, and then again in 1794, while he was accompanying troops to suppress the Whiskey Rebellion in Western Pennsylvania.

Built between 1819 and 1826, the Menai Bridge was the major structure on Britain's strategically important Holyhead Road connecting London with Holyhead and by sea to Ireland. Designed by Thomas Telford, the bridge's main span was 579 feet from tower to tower, the longest that had ever been attempted at this time. He used four sets wrought-iron eyebars to suspend the deck. These were made by William Hazledine at his Upton forge near Shrewsbury. Each bar was carefully tested in his Coleham shops before being pinned together and lifted into place.

Traversing the Great Glen of the Scottish Highlands for 60 miles the Caledonian Canal connects the North Sea by Beauly and Moray Firth on the east coast with the Irish Sea by Lochs Linnhe and Eil on the west. Thirty eight miles of the canal pass through freshwater lochs Douchfour, Ness, Oich and Lochy with the remaining 22 miles formed by earth cutting. Initially 28 locks, and later 29, were required to reach the summit elevation of 106 feet at Loch Oich.

This silver mine preserves two features of bygone practice. One is the reversible waterwheel of the ore-hoist, which originally was installed in 1565 and currently dates back to 1824. The present wheel is 9 meters in diameter and reaches a depth of 700 meters.

Much of the sophisticated system of canals, dams, gates, and tunnels built to manage water power in 19th-century Lowell is preserved today as the basis of the Lowell National Historical Park and the Lowell Heritage State Park. Pictured above is the Boott Penstock, an early channel adjacent to…
Read More
Kinematics is the study of geometry of motion. Reuleaux designed the models in the Cornell collection as teaching aids for invention, showing the kinematic design of machines. The mechanisms in the collection represent the fundamental components of complex machines and were conceived as elements…
Read More
Montogomery Bell was a land developer and iron maker who purchased the Harpeth Narrows site to expand his industrial empire - which ultimately consisted of 14 iron blast furnaces throughout middle Tennessee.
The Harpeth River makes a tight bend around a steep limestone ridge, losing 17…
Read More

The Atlantic Ocean's northward-flowing Gulf Stream meets the southward-flowing Labrador Current at a point marked approximately by North Carolina's Outer Banks. Since the earliest days of United States commerce, shifting tides, inclement weather, treacherous shoals, and a low-lying shoreline…
Read More
The Carrollton Viaduct over Gwynn's Falls was the first masonry railroad viaduct constructed in the United States. This structure proved the feasibility of using a viaduct to transport railway vehicles across wide and deep valleys.
The concept for the viaduct came from international…
Read More
The Chesapeake & Delaware Canal is the only canal built in 19th-century America that still operates today as a major shipping route. Connecting the Port of Baltimore and Upper Chesapeake Bay with the mouth of the Delaware River and the Port of Philadelphia, the canal was one of the first…
Read More

When a new road bridge was constructed alongside it, plans were made to demolish the Conwy Suspension Bridge. There was a national outcry and, since 1958, the bridge has been in the care of the National Trust and closed to vehicular traffic.
Designed by Thomas Telford in the…

This elegant cast iron arch bridge designed by Scotland's famous Thomas Telford was built from 1812 to 1814. It is the earliest surviving example of a portable lattice-braced standard type that Telford developed for use at wide and deep water crossing sites unsuitable for masonry spans…

The Dismal Swamp Canal was created as a 22-mile waterway, extending from Deep Creek, Virginia to South Mills, North Carolina. The canal enabled North Carolina producers of building and agricultural products to deliver goods to the Port of Norfolk where they were transferred to ocean-going…

In its day, the famous Erie Canal was the world's longest canal and America's greatest engineering feat. It was the principal route for emigrants from the East and agricultural products from the West. Before construction of the canal, New York City was the nation's fifth largest seaport, behind…
Read More
At a time when steam power was finding its first uses in America, Philadelphia opened two steam pumping stations, January 1801, to lift water from the Schuylkill River and distribute it through the city's wooden pipes and mains. By 1811 a new water power works was begun on the river near Morris…
Read More
The Gota Canal is the biggest infrastructure project ever built in Sweden. The canal was dug by hand with shovels made of wood. It took over 22 years of 12-hour days - an estimated 12 million man-days of labor - to complete the project.
The Gota (pronounced yeu-ta) Canal is a 347-…
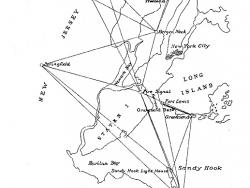
The precise system of measurements provided today by the U.S. Coast and Geodetic Survey originated with an act of Congress under the administration of Thomas Jefferson in 1807 that funded work on "an accurate chart" of America's coastal waters. Intended to aid sea-going commerce, the…

While the Erie Canal has become well-known in the annals of American history, the Middlesex Canal, built two decades earlier and a model for canal engineers throughout young America, has only recently become recognized for its important achievements. Extending 27 miles northeast from Boston…
Read More
In 1794, Congress authorized and President Thomas Jefferson signed into law the raising of a Corps of Artillerists and Engineers (now the United States Army Corps of Engineers) to be educated and stationed at the newly created United States Military Academy. The U.S. Military Academy was the…
Read More

The National Road was the first interstate highway in the United States, and the first roadway to be financed with federal money. Authorized by Congress during the administration of Thomas Jefferson in 1806, the road was built over time and in sections from Cumberland, Maryland, westward through…
Read More

