Prior to its merger with the Carnegie Institute of Technology in 1967 to form Carnegie Mellon University, the nonprofit Mellon Institute for Industrial Research was a major, independent research corporation dedicated to promoting applied research for industry and educating scientific researchers for the benefit of society as a whole. The Institute educated hundreds of fellows for careers in industrial research and helped to sell the very idea of research to manufacturers.
USA

Rachel Carson’s Silent Spring, published in 1962, was a landmark in the development of the modern environmental movement. Carson’s scientific perspective and rigor created a work of substantial depth and credibility that sparked widespread debate within the scientific community and the broader public about the effect of pesticides on the natural world. These discussions led to new policies that protect our air, our water, and, ultimately, our health and safety.

The American Chemical Society, the world’s largest scientific society, celebrated its 125th anniversary in 2001. Founded in 1876 in New York City, the Society now has 186 local sections in all 50 states, international chapters, and 32 technical divisions that bring together scientists with interests ranging from small business to environmental protection.
The text of the plaque commemorating the landmark reads:

Izaak Maurits Kolthoff (1894–1993) has been described as the father of modern analytical chemistry for his research and teaching that transformed the ways by which scientists separate, identify, and quantify chemical substances. Once a collection of empirical recipes and prescriptions, the field of analytical chemistry is today an essential branch of chemistry built upon solid theoretical principles and experimental techniques, the basis of which was formed over the course of Kolthoff’s nearly 80-year career.

As much as we know today about the planets of the solar system, it’s almost incomprehensible that a mere 50 years ago we knew almost nothing about them. Observations of even Mars and Venus, Earth’s closest planetary neighbors, through Earth-based telescopes had provided only the most rudimentary information on their physical characteristics and essentially no information on the chemical properties of the planets and their atmospheres.
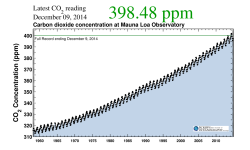
Charles David Keeling of Scripps Institution of Oceanography was the leading authority in establishing the global atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) record. In 1958, Keeling began measuring atmospheric CO2 concentrations from Hawaii’s Mauna Loa Observatory. Using rigorous analytical procedures, he revealed new information about natural and man-caused carbon trends.

Frozen foods have become a staple of the modern diet. Freezing allows consumers to have access to foods previously unavailable or available only seasonally, and it provides convenience for many families. But frozen foods became commonplace only after World War II, in part due to research conducted at the Western Regional Research Center which helped determine the proper time and temperature at which various foods should be frozen to insure their quality and stability.
The plaque commemorating the research reads:

Instant mashed potatoes are commonplace on grocery shelves and have found wide use institutionally and in domestic and international food aid programs. The most successful form of instant mashed potatoes resulted from the flake process developed in the 1950s and 1960s at the Eastern Regional Research Center, a United States Department of Agriculture facility outside of Philadelphia. The process for reconstituting instant mashed potatoes devised at this facility utilized dehydration technology.
The first commercial circulating fluid bed reactor, PCLA #1 (Powdered Catalyst Louisiana), went on stream on May 25, 1942, in the Baton Rouge Refinery of the Standard Oil Company of New Jersey (now ExxonMobil Corporation). This first use of powdered catalysts in continuous operation allowed the efficient cracking of heavy gas oils to meet the growing demand for high-octane fuels. Today, fluid bed reactors are in use worldwide for the manufacture of fuels, chemical intermediates and plastics.
The plaque commemorating the development reads:
Era_date_from:

Flavor—encompassing both aroma and taste—provides the defining characteristic of how we experience food. Flavor has long been an enigma to scientists: Aristotle described two categories of taste, sweet and bitter. Today we recognize five basic tastes in food: sweetness, saltiness, sourness, bitterness and umami (savory). But what are the scientific components of flavor, and how can flavor be studied, quantified and replicated?

Like other American cities in the late 19th century, Baltimore had grown so quickly its supply system was unable to provide city residents with a dependable supply of water. Two reservoirs built outside the city helped increase capacity, but heavy rainfalls in the largely agricultural area…
Read More
The significance of the 15-mile Whitewater Canal was not in its ability to create a profit, but rather its effect on the economic growth of the Whitewater River Valley, considered the gateway to the interior of Indiana. Before the canal, travel was challenging. Most waterways in Indiana…

Not only was Dunlap's Creek Bridge the first cast-iron bridge in America, it was the first metal bridge anywhere to use what its builder, Capt. Richard Delafield, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, described as "standardized, interchangeable, manufactured parts." The bridge was built as part…

Designed by Sam Diescher, son-in-law of the Monongahela's designer John Endres, the Duquesne Incline opened May 20, 1877, as the second of seventeen built and operated in the Pittsburgh area. It has operated with only minor interruptions for the last one hundred years. A preservation group from…
Read More
The Durango-Silverton Narrow Gauge Branch of the Denver & Rio Grande Western Railroad extends from the town of Durango to the mining camp of Silverton. Built in 1882 through one of the most rugged mountain areas of the nation, its complexity remains a testament to the role civil…

In the decade following the Civil War, the Mississippi River began to lose its standing as the primary transport artery in the Midwest. Railroads were taking over, and Chicago was rapidly becoming the center of Midwestern commerce. The Eads Bridge was the first major railroad link over…

Operated by the Philadelphia Electric Company (PECO), now known as Exelon Corp., Eddystone Station Unit #1 is a 325 MW pulverized-coal-fired plant that pushed the technology of steam-electric generating plants. When built in 1960, engineers sought to make a more efficient plant using higher…
Read More
This dynamo, connected directly to a high-speed steam engine, was one of six that produced direct current at Thomas A. Edison's electric power station at 257 Pearl Street in New York City. The Pearl Street Station was the prototype for central station power generation. Edison set out in 1878 to…
Read More
Edison's simple and unprecedented instrument allowed for the first time the permanent recording and reproduction of sound, especially the human voice. On December 6, 1877, Edison put tinfoil around the cylinder, turned the handle of the shaft and, shouting into one of the diaphragms, recorded a…
Read More
Established in 1935 as the Valparaiso Bombing and Gunnery Base, the base supported the U.S. Army Air Corps, the predecessor to the U.S. Air Force, as its primary facility for training new pilots in bombing and gunnery tactics. It also served as a test facility for aircraft, aircraft armament,…
Read More
One of the first major efforts to increase farming and encourage habitation in the arid regions of the western United States, the Rio Grande Project was designed to provide reliable irrigation as well as resolve a dispute over water supply with the Republic of Mexico. The project's centerpiece…
Read MoreThe Wheeling Suspension Bridge was the first bridge to span the Ohio River. It was initially completed in 1849, but destroyed by a tornado five years later. The bridge was rebuilt in 1856. The replacement bridge has the same general appearance of the original structure; the massive towers,…
Read More
The stone was set by the joint U.S.-Spanish survey party on April 10, 1799. Made of sandstone, it is roughly two feet high and eight inches thick. On the north side of the stone is the inscription "U.S. Lat. 31, 1799." On the south side is "Dominio de S.M. Carlos IV, Lat. 31, 1799."
…
Read More

In its day, the famous Erie Canal was the world's longest canal and America's greatest engineering feat. It was the principal route for emigrants from the East and agricultural products from the West. Before construction of the canal, New York City was the nation's fifth largest seaport, behind…
Read More

At a time when steam power was finding its first uses in America, Philadelphia opened two steam pumping stations, January 1801, to lift water from the Schuylkill River and distribute it through the city's wooden pipes and mains. By 1811 a new water power works was begun on the river near Morris…
Read More

The Fink Deck Truss Bridge is thought to have been originally used on the Norfolk and Western mainline railway. It was moved to its present location and converted to a vehicular bridge over a railroad spur in 1893 when the Norfolk and Western mainline was moved. It was relocated again in 1985 to…
Read More


