The demonstrated success in space flight is the result of electronic technology developed at Cape Canaveral, the J. F. Kennedy Space Center, and other sites. A wide variety of advances in radar tracking, data telemetry, instrumentation, space-to-ground communications, on-board guidance, and real-time computation were employed to support the U.S. space program. These and other electronic developments provided infrastructure necessary for the successful landing of men on the moon in July 1969 and their safe return to earth.
Space

YearAdded:
Image Credit:
Courtesy Wikipedia/NASA
Image Caption:
A culmination of research in radar tracking, data telemetry, instrumentation, space-to-ground communications, on-board guidance, and real-time computation: the 1969 moon landing.
Era_date_from:
1950
2001

The Advanced Engine Test Facility was built in 1964, three years after President John F. Kennedy committed the United States to world leadership in aeronautical science. Conceived and designed by Wernher von Braun, the first director of the Marshall Space Flight Center, this facility was used to perform static tests on the booster of the Saturn V rocket, which launched Apollo 11 to the moon on July 16, 1969.
The stand has four concrete legs, each four feet thick and rising 144 feet to a steel superstructure supporting a 200-ton crane.
YearAdded:
Image Credit:
Courtesy ASME
Image Caption:
Saturn V Rocket being lifted onto the A-2 Test Stand at NASA's John C. Stennis Space Center
Era_date_from:
1964
1993

The Atlas E-2 Space Booster, or launch vehicle, is a modified intercontinental ballistic missile developed by the Convair Division of General Dynamics and the U.S. Air Force. The basic concept of the Atlas system was proven in its first flight on June 11, 1957, followed over the years by the launching more than five hundred vehicles including the Pioneer, Ranger, Mariner, and Surveyor. Many payloads were sent into orbit as detachable sections of Atlas missiles.
YearAdded:
Image Credit:
All 3 images are Public Domain
Image Caption:
A compilation of three successful launches vehicles in action. On the left is the Atlas-Centaur, the center is the Atlas-Agena, and the right is the SM-65A Atlas missile.
Era_date_from:
1957
1985

6225 Vectorspace Blvd Titusville State: FL Zip: 32780 Country: USA Website: http://www.asme.org/about-asme/history/landmarks/topics-a-l/air-and-space-transportation/-162-apollo-space-command-module-%281968%29, http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/planetary/lunar/apollo14info.html Creator: North American Aviation
The Apollo was the vehicle that first transported humans to the moon and safely back to earth. Nine lunar flights were made between 1968 and 1972. The command module, built by North American Aviation (at the time of launch, North American Rockwell Corporation), accommodated three astronauts during the mission. It was the only portion of the Apollo spacecraft system designed to withstand the intense heat of atmospheric re-entry at 25,000 mph and complete the mission intact. This command module at Rockwell flew as Apollo 14 in 1971.
YearAdded:
Image Credit:
Courtesy Flickr/Chad Nordstrom (CC BY 2.0)
Image Caption:
The real Apollo Space Command Module on display at the Kennedy Space Center's Saturn V Building.
Era_date_from:
1968
1992

The Apollo lunar module (LM-13) was developed by the Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corp. (now Northrop Grumman). The LM's main functions were to carry two astronauts from lunar orbit to the moon's surface, and then return them to lunar orbit to rendezvous and dock with the Apollo command-service modules. On the surface, the LM served as a shelter and base of operations as the astronauts carried out their exploration and experiments. On July 20, 1969, the LM "Eagle" touched down on the moon, becoming the first piloted spacecraft to land on a celestial body other than Earth.
YearAdded:
Image Credit:
Courtesy Flickr/Michael Gray (CC BY-SA 2.0)
Image Caption:
The Apollo Lunar Module LM-13 on display in the Cradle of Aviation Museum
Era_date_from:
1972
2002

"Driven by the need to understand the characteristics of radio communication in Canada's North, Canadian researchers focused on the exploration of the earth's upper atmosphere, the ionosphere. Canada's satellite program commenced with the launch of Alouette-I on September 29, 1962. Alouette-II followed in 1965, ISIS-I in 1969, ISIS-II in 1971. The Alouette/ISIS tracking antenna serves as a reminder of Canada's contribution to this international effort in space science.
YearAdded:
Image Credit:
Public Domain; NASA
Image Caption:
The The Alouette 1, the very first satellite constructed by Canada
Era_date_from:
1962
1993
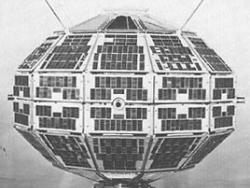
"Driven by the need to understand the characteristics of radio communication in Canada's North, Canadian researchers focused on the exploration of the earth's upper atmosphere, the ionosphere. Canada's satellite program commenced with the launch of Alouette-I on September 29, 1962. Alouette-II… Read More

The Apollo lunar module (LM-13) was developed by the Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corp. (now Northrop Grumman). The LM's main functions were to carry two astronauts from lunar orbit to the moon's surface, and then return them to lunar orbit to rendezvous and dock with the Apollo command-service… Read More

The Apollo was the vehicle that first transported humans to the moon and safely back to earth. Nine lunar flights were made between 1968 and 1972. The command module, built by North American Aviation (at the time of launch, North American Rockwell Corporation), accommodated three astronauts during… Read More

The Atlas E-2 Space Booster, or launch vehicle, is a modified intercontinental ballistic missile developed by the Convair Division of General Dynamics and the U.S. Air Force. The basic concept of the Atlas system was proven in its first flight on June 11, 1957, followed over the years by the… Read More

The Advanced Engine Test Facility was built in 1964, three years after President John F. Kennedy committed the United States to world leadership in aeronautical science. Conceived and designed by Wernher von Braun, the first director of the Marshall Space Flight Center, this facility was used to… Read More

The demonstrated success in space flight is the result of electronic technology developed at Cape Canaveral, the J. F. Kennedy Space Center, and other sites. A wide variety of advances in radar tracking, data telemetry, instrumentation, space-to-ground communications, on-board guidance, and real…
Read More

