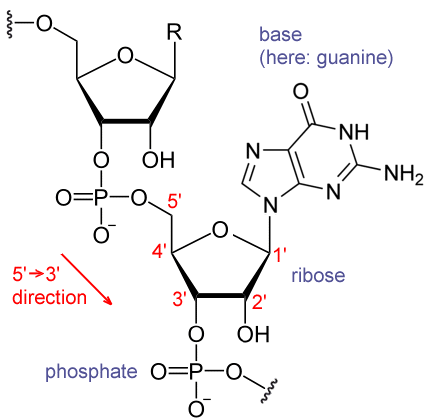
In 1961, in the National Institutes of Health Headquarters (Bethesda, MD), Marshall Nirenberg and Heinrich Matthaei discovered the key to breaking the genetic code when they conducted an experiment using a synthetic RNA chain of multiple units of uracil to instruct a chain of amino acids to add phenylalanine. The uracil (poly-U) served as a messenger directing protein synthesis. This experiment demonstrated that messenger RNA transcribes genetic information from DNA, regulating the assembly of amino acids into complex proteins. Nirenberg would go on to decipher the code by demonstrating the correspondence of various trinucleotides to individual amino acids. He was a co-winner of the Nobel Prize in 1968.